Molding software configuration
The font modulo software used in the test example is PCtoLCD2002. For detailed instructions on its use, see the following document:
PCtoLCD2002 Instructions for use
The PCtoLCD2002 software is specifically set as follows:
- Font and size selection
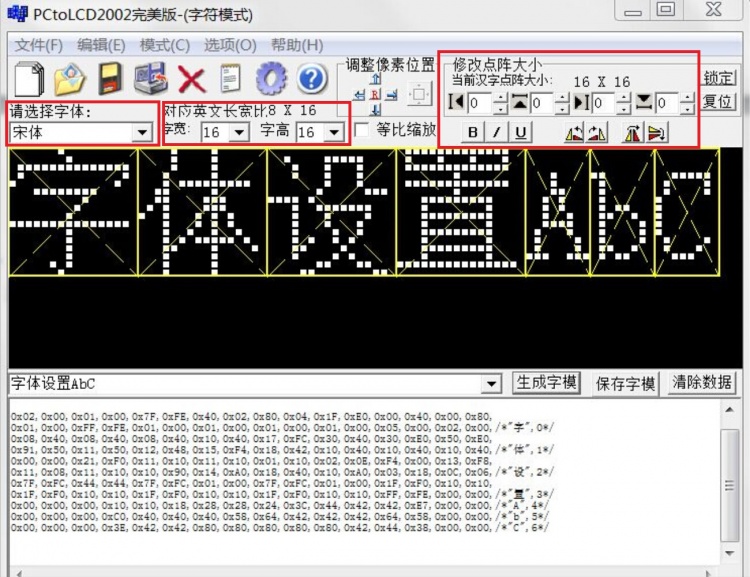
- Mode needs to select 字符模式
- Fonts can be selected according to needs, such as selection 宋体
- The word width and word height can be selected according to the needs. The font sizes commonly used in Chinese and English are as follows:
- Chinese (word width x word height):16x16、24x24、32x32、48x48
- English (character x word height):6x8、6x12、8x16、12x24、16x32、24x48(The corresponding font size needs to be set to respectively12x8、12x12、16x16、24x24、32x32、48x48)
- Modify the dot matrix size can be set according to requirements, generally set to 0
- Font option setting
- There are many situations in the Chinese and English font option setting. Different settings and different code processing methods.
- Here is an example of the following settings, the subsequent function code is written based on this setting.
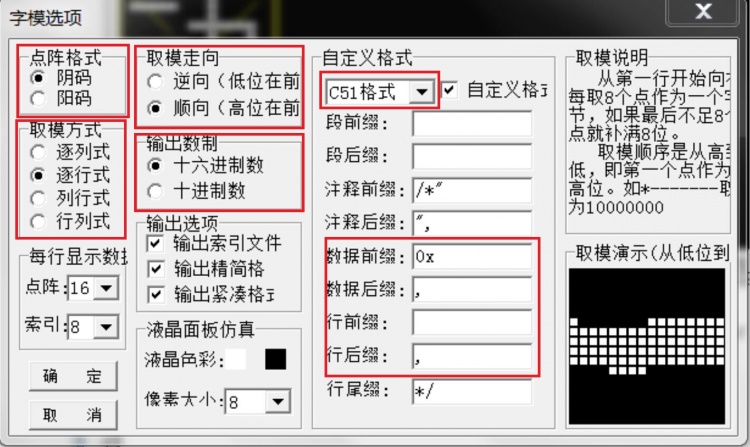
- Dot matrix format select 阴码
- Modal mode select 逐行式
- Molding trend select 顺向(高位在前)
- Output number system select 十六进制数
- Custom format select C51格式
Bottom support function
- LCD_SetWindows
- The function implementation differs depending on the driver IC (different drive ICs set coordinate values with different commands and principles),
- but the principle is basically the same, setting the start and end coordinates and setting a display area.
- Examples are as follows (ILI9341 as an example)
void LCD_SetWindows(u16 xStar, u16 yStar,u16 xEnd,u16 yEnd)
{
LCD_WR_REG(lcddev.setxcmd);
LCD_WR_DATA(xStar>>8);
LCD_WR_DATA(0x00FF&xStar);
LCD_WR_DATA(xEnd>>8);
LCD_WR_DATA(0x00FF&xEnd);
LCD_WR_REG(lcddev.setycmd);
LCD_WR_DATA(yStar>>8);
LCD_WR_DATA(0x00FF&yStar);
LCD_WR_DATA(yEnd>>8);
LCD_WR_DATA(0x00FF&yEnd);
LCD_WriteRAM_Prepare(); //Start writing to GRAM
}
- Lcd_WriteData_16Bit
- This function is to set the pixel color value into GRAM, and then display it
- Examples are as follows (ILI9341 as an example)
void Lcd_WriteData_16Bit(u16 Data)
{
LCD_CS_CLR;
LCD_RS_SET;
SPI_WriteByte(SPI2,Data>>8);
SPI_WriteByte(SPI2,Data);
LCD_CS_SET;
}
- LCD_DrawPoint
- In fact, the LCD_SetWindows function and the Lcd_WriteData_16Bit function are used to display a pixel.
- Examples are as follows (ILI9341 as an example)
void LCD_DrawPoint(u16 x,u16 y)
{
LCD_SetCursor(x,y);//Set the cursor position
Lcd_WriteData_16Bit(POINT_COLOR);
}
English character modulo
- 1.Because in the program, the English characters that need to be displayed are searched according to the ASCII offset,
- so the entire set of ASCII characters needs to be modeled.
- 2.If you do not need to use a character, you can set the modulo data of the character to {0},
- as shown in the following example (take 6x8 size characters as an example)
const unsigned char asc2_0806[95][8]={
... //This example is omitted, the actual application needs to be added
{0},/*"2",18*/ Do not use number 2
{0x00,0x00,0x78,0xB0,0x08,0x88,0x70,0x00},/*"3",19*/
{0x00,0x00,0x30,0x50,0x90,0x78,0x10,0x00},/*"4",20*/
{0},/*"5",21*/ Do not use number 5
{0x00,0x00,0x70,0x80,0xF8,0x88,0x70,0x00},/*"6",22*/
{0},/*"7",23*/ Do not use number 7
{0x00,0x00,0xF8,0x88,0x70,0x88,0x78,0x00},/*"8",24*/
{0},/*"9",25*/ Do not use number 9
... //This example is omitted, the actual application needs to be added
}
- 3.The ASCII characters are as follows (the first space is also included):
- ASCII characters: !"#$%&'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~
- 4.The English modulo data fonts are all Default
- The different sizes of English character modulo description
Chinese character modulo
- 1.When displaying Chinese characters, the modulo data is obtained by querying the GBK code that needs to display Chinese characters;
- 2.After the Chinese character is successfully modulo, the corresponding relationship between the Chinese character GBK code and the modulo data is saved through an array of structures.
- 3.The structure is defined as follows:
//16x16 Chinese font structure definition
typedef struct
{
unsigned char Index[2]; //Store Chinese character GBK code
char Msk[32]; //Store Chinese character modulo data
}typFNT_GB16; //Structure name can be defined by yourself
\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\
//24x24 Chinese font structure definition
typedef struct
{
unsigned char Index[2]; //Store Chinese character GBK code
char Msk[72]; //Store Chinese character modulo data
}typFNT_GB24; //Structure name can be defined by yourself
\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\
//32x32 Chinese font structure definition
typedef struct
{
unsigned char Index[2]; //Store Chinese character GBK code
char Msk[128]; //Store Chinese character modulo data
}typFNT_GB32; //Structure name can be defined by yourself
\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\
//48x48 Chinese font structure definition
typedef struct
{
unsigned char Index[2]; //Store Chinese character GBK code
char Msk[288]; //Store Chinese character modulo data
}typFNT_GB48; //Structure name can be defined by yourself
- The different sizes of Chinese modulo description
